What Is an E-Signature and Is It Legally Binding? A Complete Guide
Wondering if e-signatures are legally valid? This guide explains how they work and why they're trusted for signing documents online.

Anthony Merulla
What Are E-Signatures and How Do They Work?
The simple definition of an e-signature is any method of signing a document electronically, instead of with pen and paper. In technical terms, an electronic signature is a digital sign of a person's intent to agree to the contents of a document.
A physical signature requires ink and paper. An e-signature lets you sign documents online with your computer, phone, or tablet. Electronic signatures come in many forms: you can type your name, draw your signature on a screen, or even paste an image of your handwritten signature. Each method proves you've agreed to the document.
Forms and Technologies Used for E-Signatures
E-signatures vary from simple to highly secure. Here's a breakdown:
- Simple e-signatures: Typing your name, clicking an 'I Agree' button, or pasting an image.
- Advanced electronic signatures: Require stronger proof, such as login credentials or codes sent to your phone.
- PKI Digital Signatures: Using Encryption and Certificates for Maximum Security These are required for some regulated transactions.
- Qualified electronic signatures: Meet even stricter rules and rely on a trusted digital certificate to prove identity. These are often the most secure and widely accepted type.
Leading e-signature platforms include audit trails. An audit trail shows who signed, when, and from where. Authentication features such as passwords, email confirmation, or SMS codes add another layer of trust.
Where E-Signatures Are Commonly Used
More organizations are turning to e-signatures for a wide range of documents:
- Sales contracts and purchase agreements
- HR onboarding paperwork: job offers, benefits forms
- Legal documents: NDAs, POs, loan agreements
- Consent forms for healthcare or research
- Financial services applications and insurance forms
E-signatures save time and reduce paperwork. Companies use them to sign documents online, speed up workflows, and maintain better records.
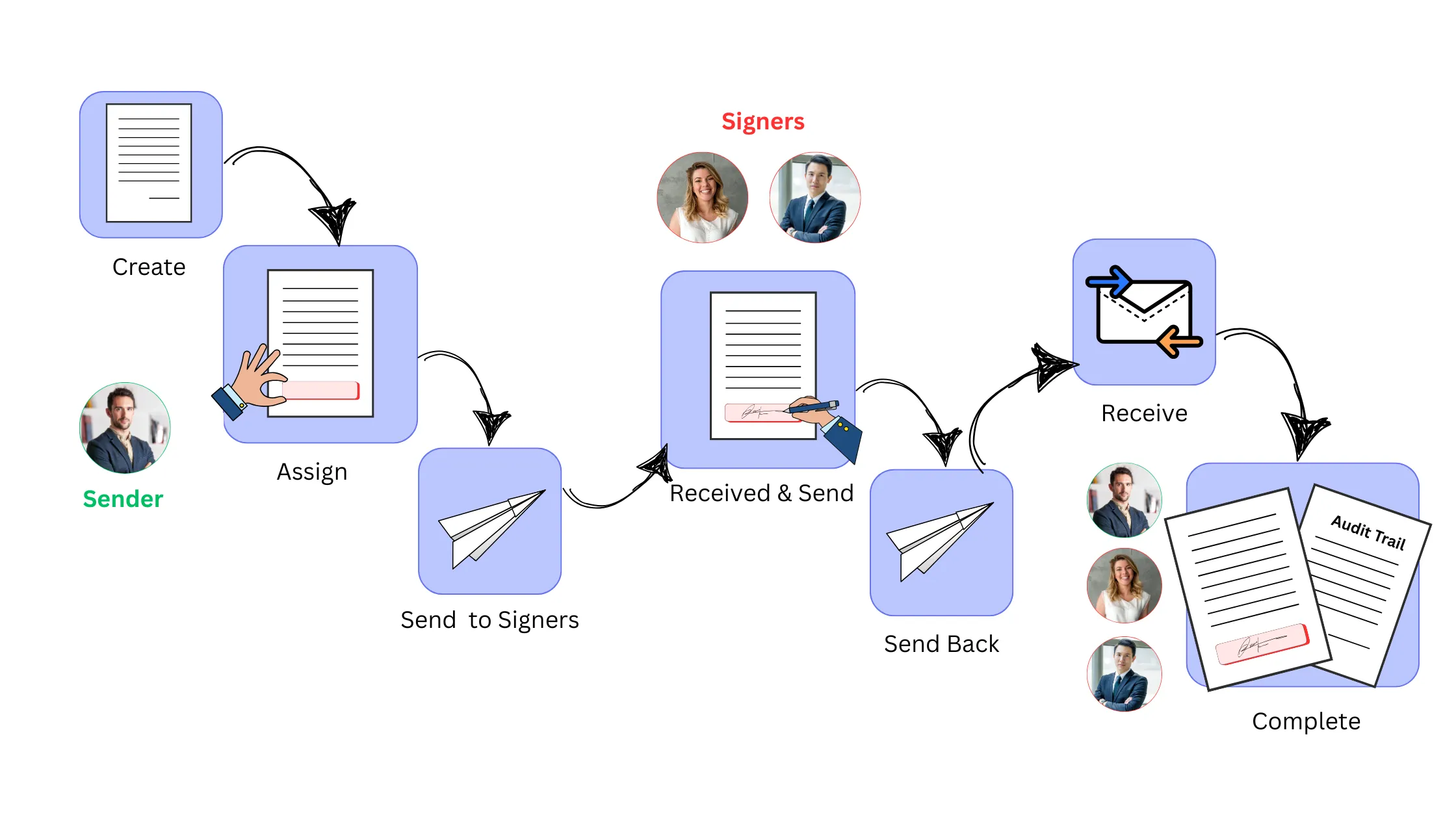
How Do E-Signatures Work Step-by-Step?
The process of e-signing is straightforward. Here's how it usually works:
- Create Document: The sender begins by creating or uploading the file to an e-signature platform.
- Assign Fields: The sender places signature, date, initials, or other required fields where needed in the document.
- Send to Signers: The document is securely sent to recipients via email or a unique signing link.
- Receive and Send: Signers receive the document, review the content, sign using a mouse, finger, or typed name, and send it back instantly.
- Send Back Signed: The signed document is automatically routed back to the sender or to the next signer in sequence.
- Receive Confirmation: The sender is notified that the document has been signed and returned.
- Complete Process: All parties receive a finalized signed copy and a detailed audit trail with timestamps for recordkeeping and compliance.
Technologies involved:
- Encryption: Protects documents during transfer and storage.
- Identity Check: Email or SMS codes help confirm each signer's identity.
- Audit trails: Record every step, showing who did what and when.
For example, Tools like Inkfree, PandaDoc, DocuSign, and SignNow combine strong encryption with a streamlined signing workflow. They keep documents secure while making them easy to sign for everyone involved.
Are E-Signatures Legally Binding?
Yes, e-signatures are legally binding in most settings. Major regulations in the United States (ESIGN Act, UETA) and Europe (eIDAS) give e-signatures the same legal standing as handwritten signatures for most documents.
- E-signatures can be used for:
- Business contracts
- Employment agreements
- Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs)
- Real estate transactions
But not every document can use an e-signature. Some records, like wills or marriage certificates, may still require paper signatures by law.
For more on the legal status of e-signatures in the U.S., check out Adobe's guide to electronic signature laws & regulations.
Key Laws and Regulations Governing E-Signatures
ESIGN Act (U.S.): Grants e-signatures the same legal value as ink signatures for nearly all uses.
UETA (U.S.): The Uniform Electronic Transactions Act works alongside ESIGN at the state level.
eIDAS (EU): The European standard, which recognizes simple, advanced, and qualified e-signatures. These signatures, known as 'qualified,' use trusted digital certificates and are legally the most robust.
Outside the U.S. and EU, laws vary. China, India, and many Latin American countries have their own electronic signature regulations. Always check local law if you work across borders.
What Makes an E-Signature Enforceable?
Courts look for:
- Intent: Did the signer mean to agree?
- Consent: Did all parties agree to use electronic methods?
- Authentication: Can you prove who signed?
- Integrity: Has the document changed since signing?
A full audit trail helps demonstrate these points. Some courts have even upheld digital agreements using emojis, finding that they can show a person's intent, depending on the context.
When Are E-Signatures Not Accepted?
You'll need to use traditional signatures for some documents:
- Wills and testamentary trusts
- Certain family law documents (like adoption)
- Court orders and official government filings
Check statutes and regulations before relying on an e-signature for high-risk agreements.
How Inkfree Helps You Sign Legally and Easily
Inkfree offers a secure solution trusted by professionals in law, finance, and business. Every signature comes with:
- Full audit trails: Track every step in the signing process.
- Strong signer verification: Tools like SMS codes or multifactor authentication.
- Legal compliance: Aligns with major regulations like ESIGN, UETA, and eIDAS.
Users often report faster turnaround and less paperwork. 'Inkfree helped us sign important contracts in minutes, not days,' shared one satisfied client.
Final Thoughts on E-Signatures' Legal Status
E-signatures are transforming how we sign, send, and store agreements. They're recognized by courts, protected by strong laws, and accepted for nearly every type of contract provided you meet the right requirements.
Choosing a compliant platform like Inkfree builds trust, saves time, and keeps your documents safe. For most businesses and individuals, e-signatures aren't just a digital convenience' they're a reliable, legal answer to the question: what is an e-signature and is it legally binding? The answer is clear' yes, it is.
Thinking about switching to e-signatures? Make sure you pick a solution that meets legal standards and fits your workflow. Your contracts'and your peace of mind'depend on it.
