E-Signatures vs Scanned Signatures – Which Is More Secure?
Compare e-signatures and scanned signatures to see which is more secure, legally valid, and better for protecting your documents.

Anthony Merulla
E-Signatures vs Scanned Signatures: What's More Secure?
In today's fast-paced digital world, signing documents has evolved beyond pen and paper. Businesses and individuals now face a choice between two popular methods: electronic signatures and scanned signatures.
The rise of remote work has accelerated the adoption of digital signing solutions. While many organizations have embraced secure e-signature platforms to sign PDF documents online, others still rely on the traditional method of scanning handwritten signatures.
But here's the crucial difference:
- E-signatures are created through specialized software that verifies signer identity, records signing details, and ensures document integrity.
- Scanned signatures are simply digital images of handwritten signatures, uploaded to documents without built-in security measures.
Think of it this way: using a scanned signature is like photocopying your house key - anyone with access to the copy could potentially use it. An e-signature, on the other hand, works more like a sophisticated digital lock with multiple security features built in.
Understanding these differences is essential for protecting your documents and ensuring their legal validity in our increasingly digital business environment.
Understanding Electronic Signatures

Electronic signatures are a digital way to show approval or agreement on documents. Unlike traditional ink signatures, e-signatures use advanced technology to create legally binding agreements online.
How Electronic Signatures Work:
- Unique signature identifiers are created digitally.
- The identity of the signer is securely authenticated.
- The time and location of signing are tracked.
- The document is encrypted and protected.
- An audit trail is generated.
The ESIGN Act in the United States and eIDAS Regulation in the European Union establish the legal framework for electronic signatures. These regulations grant e-signatures the same legal status as handwritten signatures when specific requirements are met.
Legal Requirements for Valid E-Signatures:
- All parties must clearly intend to sign.
- Consent to conduct business electronically is required.
- The identity of the signer must be verifiable.
- Secure storage and access of the document is necessary.
- Document integrity must be maintained after signing.
E-signature platforms implement these requirements through:
- Two-factor authentication.
- IP address tracking.
- Digital certificates.
- Encrypted document storage.
- Detailed audit logs.
Free electronic signature solutions offer basic features for personal use, while premium services provide advanced security measures and compliance features for business transactions. Your choice of e-signature platform should align with your security needs and legal requirements.
The technology behind electronic signatures continues to evolve, incorporating new security features and authentication methods to maintain document integrity and prevent fraud.
Security Features of Electronic Signatures
E-signature platforms implement robust security measures to protect document integrity and verify signer identity. Here's how these security features work:
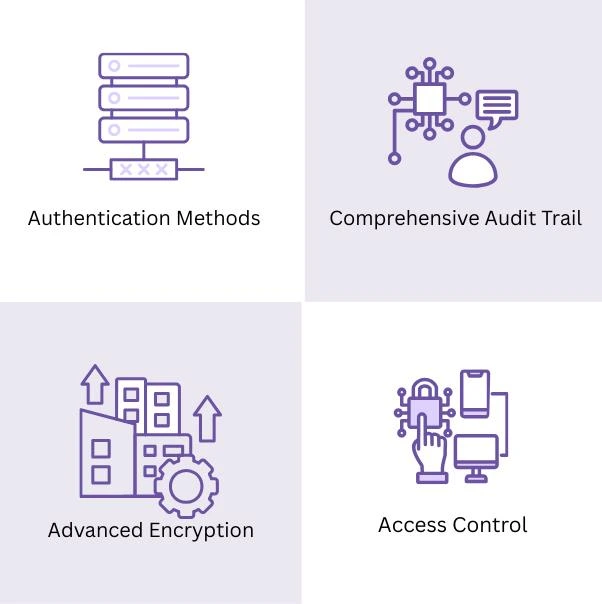
1. Authentication Methods:
- Two-factor authentication through SMS or email verification codes.
- Digital certificates linking signatures to specific individuals.
- Biometric verification options like fingerprint scanning.
- Password-protected document access.
2. Comprehensive Audit Trail:
- IP address tracking for each signing event.
- Timestamp documentation with date and time.
- Device information and location data.
- Email address verification.
- Sequential signature tracking for multiple signers.
3. Advanced Encryption:
- 256-bit AES encryption for document storage.
- SSL/TLS protocols for data transmission.
- Hash functions to detect document tampering.
- Digital signatures with public key infrastructure (PKI).
4. Access Control:
- Role-based permissions for document viewing and signing.
- Secure cloud storage with encrypted servers.
- Automatic session timeouts.
- Detailed activity logs.
These security features create a tamper-evident environment where any unauthorized changes are immediately detected and logged. The combination of authentication methods, audit trails, and encryption ensures that each signature is unique and verifiable, making electronic signatures significantly more secure than traditional scanned signatures.
Advantages of E-Signatures
E-signatures offer significant benefits that make them a superior choice for modern business operations:
1. Time and Cost Savings:
- Eliminate printing, scanning, and shipping costs.
- Sign documents instantly from any location.
- Reduce document processing time from days to minutes.
- Cut administrative overhead for document management.
2. Enhanced Accessibility:
- Sign documents from any device with internet access.
- No physical storage space required.
- Access signed documents 24/7.
- Share documents with multiple parties simultaneously.
3. Environmental Impact:
- Reduce paper consumption.
- Lower carbon footprint from shipping.
- Minimize physical storage requirements.
- Support sustainable business practices.
4. Improved Business Operations:
- Track document status in real-time.
- Automate signature reminders.
- Integrate with existing business systems.
- Standardize signing processes across departments.
5. Better Customer Experience:
- Simple, intuitive signing process.
- No special software required.
- Mobile-friendly signing options.
- Quick completion of transactions.
The combination of these advantages makes e-signatures an essential tool for businesses looking to streamline their operations while maintaining security and compliance standards.
Risks of Scanned Signatures
Scanned signatures have significant security vulnerabilities that can put your documents at risk. Here are the key security concerns:
1. Easy to Copy and Forge:
- Anyone with basic image editing skills can extract and replicate a scanned signature.
- No built-in verification methods to detect copied signatures.
- Multiple unauthorized uses possible once a signature is obtained.
2. No Authentication Process:
- No way to verify the actual signer's identity.
- Impossible to prove when or where the signature was actually made.
- Lack of timestamp or IP address tracking.
3. Document Integrity Issues:
- No protection against document alterations after signing.
- Changes can be made without detection.
- Multiple versions of the same document can exist.
4. Legal Challenges:
- Difficult to prove authenticity in legal disputes.
- Limited admissibility as evidence in court.
- No audit trail to support claims of legitimacy.
5. Storage and Management Risks:
- Vulnerable to data breaches when stored as image files.
- No encryption protection for signature files.
- Risk of unauthorized access through shared folders or email attachments.
These security gaps make scanned signatures particularly risky for high-value transactions, legal documents, or any situation where document authenticity is crucial. The lack of security features can lead to financial losses, legal complications, and damaged business relationships.
Choosing the Right Signature Method for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate signature method depends on your specific business requirements and legal obligations. Physical documents serve as crucial originals in certain industries, while digital copies provide accessible backups for quick reference and sharing.
Hybrid Approach Benefits:
- Maintain paper originals for regulatory compliance.
- Store digital versions for easy access and distribution.
- Accommodate traditional clients who prefer ink signatures.
- Create backup copies for disaster recovery.
Digital-First Strategy:
- Use e-signatures for standard business operations.
- Keep scanned copies of legacy paper documents.
- Enable remote signing capabilities.
- Reduce storage and courier costs.
Inkfree Security Features:
- 256-bit encryption protects document storage.
- Comprehensive audit trails track all document activities.
- Role-based access control limits document visibility.
- Multi-factor authentication verifies signer identity.
- Tamper-evident seals detect unauthorized changes.
Your document security strategy should align with your business processes, client preferences, and industry regulations. Consider implementing both methods strategically to maximize efficiency while maintaining security standards. Furthermore, adopting a data privacy and security framework for client document handling can significantly enhance your document management practices.
Conclusion
E-signatures are clearly more secure than scanned signatures. With strong authentication methods, encrypted storage and detailed audit trails, e-signatures are nearly impossible to tamper with. They are also legally recognized in over 60 countries, providing extra assurance for business transactions.
While scanned signatures may seem convenient, they lack the necessary security features required in today's digital world. Relying on simple image copies of signatures puts document integrity and legal validity at risk.
Ready to enhance your document security?
- Switch to a reliable e-signature solution.
- Protect your business from signature fraud.
- Speed up your signing processes.
- Ensure legal compliance across borders.
Take the first step toward secure, legally binding signatures. Try Inkfree's enterprise-grade e-signature platform and experience the difference in document security, compliance, and efficiency.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the difference between e-signatures and scanned signatures?
E-signatures are digital representations of a person's intent to sign a document, authenticated through secure methods like two-factor authentication and encryption, whereas scanned signatures are simply images of handwritten signatures uploaded onto documents without inherent security features.
Are electronic signatures legally binding?
Yes, electronic signatures are legally binding under regulations such as the ESIGN Act in the US and the **eIDAS Regulation** in the EU, provided conditions like signer consent and document integrity are met.
How do e-signature solutions ensure the security of signed documents?
E-signature platforms authenticate signer identities using methods like digital certificates and two-factor authentication, capture detailed audit trails including IP addresses and timestamps, and employ encryption techniques to prevent tampering or unauthorized access.
What are the risks associated with using scanned signatures?
Scanned signatures lack robust authentication and encryption, making them vulnerable to forgery, unauthorized use, and disputes over authenticity due to the absence of secure audit trails.
When should I choose e-signatures over scanned signatures?
E-signatures are preferable for enhanced security, legal compliance, and efficient dispute resolution. However, scanned signatures may still be used when clients prefer traditional methods or when physical originals are required alongside digital copies.
How does Inkfree protect my documents when using e-signatures?
Inkfree secures your documents by providing encrypted storage, maintaining a full audit trail of all signing activities, and implementing role-based access controls to ensure only authorized individuals can view or modify signed documents.
